Parameterize your Configuration
GoCD allows you to parameterize your pipelines and pipeline templates. This powerful feature can help reduce repetition within your configurations and also allows for complex setups using a combination of parameters and pipeline templates.
Using Web Interface
Edit the Parameters tab when defining a pipeline .
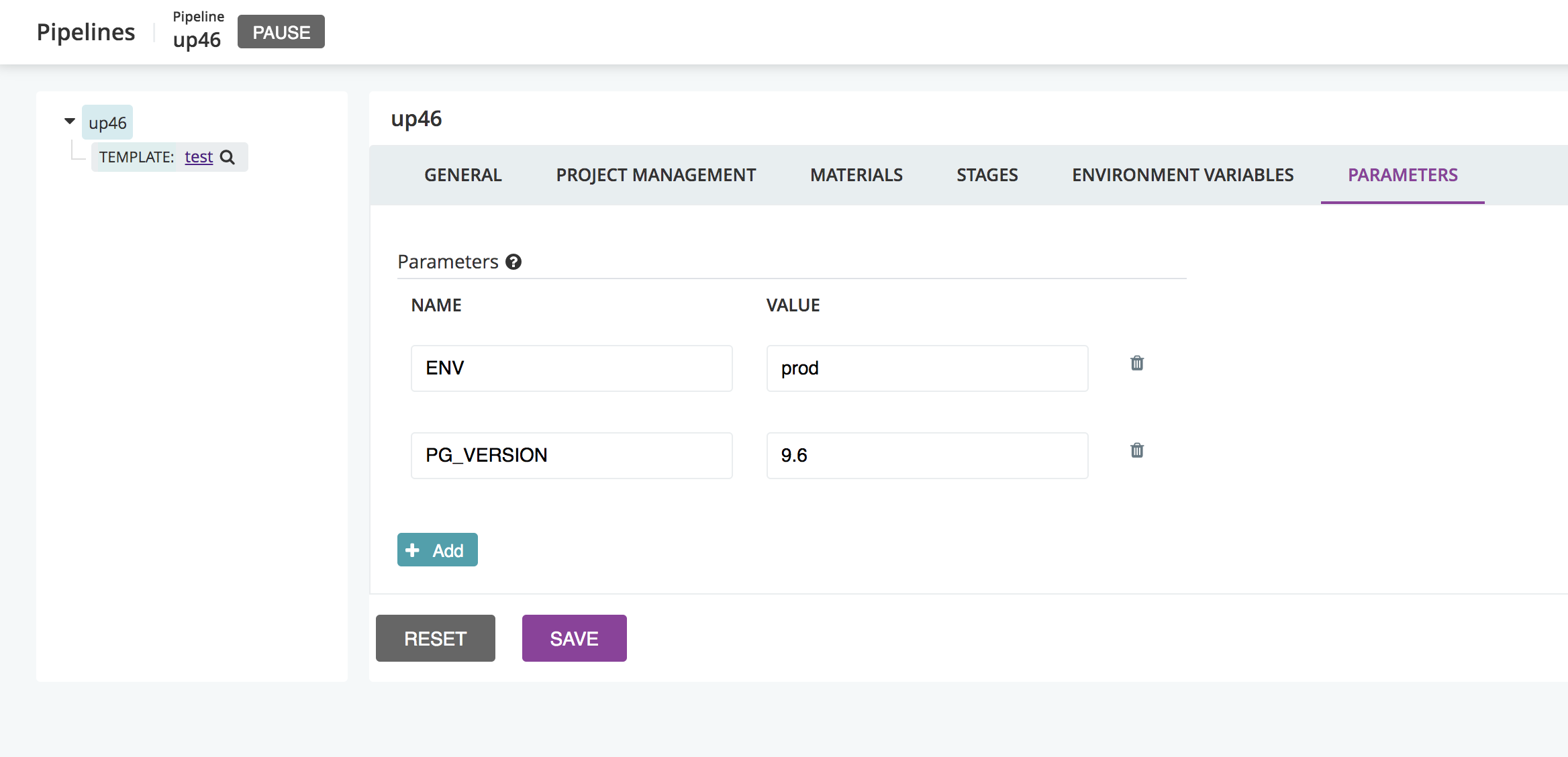
Defining and using a parameter
Parameter values are defined in the <params> tag within a pipeline and can be used anywhere within that pipeline using #{param_name}. The following example defines a new parameter called “myParam” and uses it in a job.
<pipeline name="my_pipeline">
<params>
<param name="myParam">hello world</param>
</params>
<stage name="my_stage">
<jobs>
<job name="my_job">
<tasks>
<exec command="echo" args="#{myParam}"/>
</tasks>
</job>
</jobs>
</stage>
</pipeline>
NOTE: If you want to use the # literal, you can escape it using another # literal. For example, if the parameter “foo” has the value “one”, then:
| String | Evaluates to |
|---|---|
| #{foo} | one |
| ##{foo} | #{foo} |
| ###{foo} | #one |
Using parameters in pipeline templates
Parameter usage within templates is similar to usage within pipelines. The only difference is that you cannot define parameters in a template.
<pipeline name="trunk" template="my_template">
<params>
<param name="WORKING_DIR">trunk</param>
</params>
...
</pipeline>
<pipeline name="branch" template="my_template">
<params>
<param name="WORKING_DIR">branch</param>
</params>
...
</pipeline>
The parameter defined above is used the template below.
<pipeline name="my_template">
<stage name="my_stage">
<jobs>
<job name="my_job">
<tasks>
<exec command="echo" args="Updating code from svn repository svn://codebase/#{WORKING_DIR}"/>
</tasks>
</job>
</jobs>
</stage>
</pipeline>
Rules around usage of parameters
While parameters are generally very flexible, there are some restrictions.
You cannot use a parameter to define:
- Pipeline name
- Stage name
- Job name
- A Job’s property name
- The
<runif>configuration for a job’s task - Another parameter (i.e. you cannot define a parameter using another parameter)
- Pipeline template name
- Material name
- Material passwords (however, for Git and Mercurial, passwords are not captured as separate attribute, hence can be parameterized)
- Trigger-type for Stage
Other restrictions:
- Parameters can currently only be defined within a pipeline.
- A parameter cannot be composed with another parameter i.e. #{foo#{bar}} will not be evaluated recursively.
- If a parameter is referenced but is not defined, then the configuration is invalid (Go will not let you save an invalid configuration).